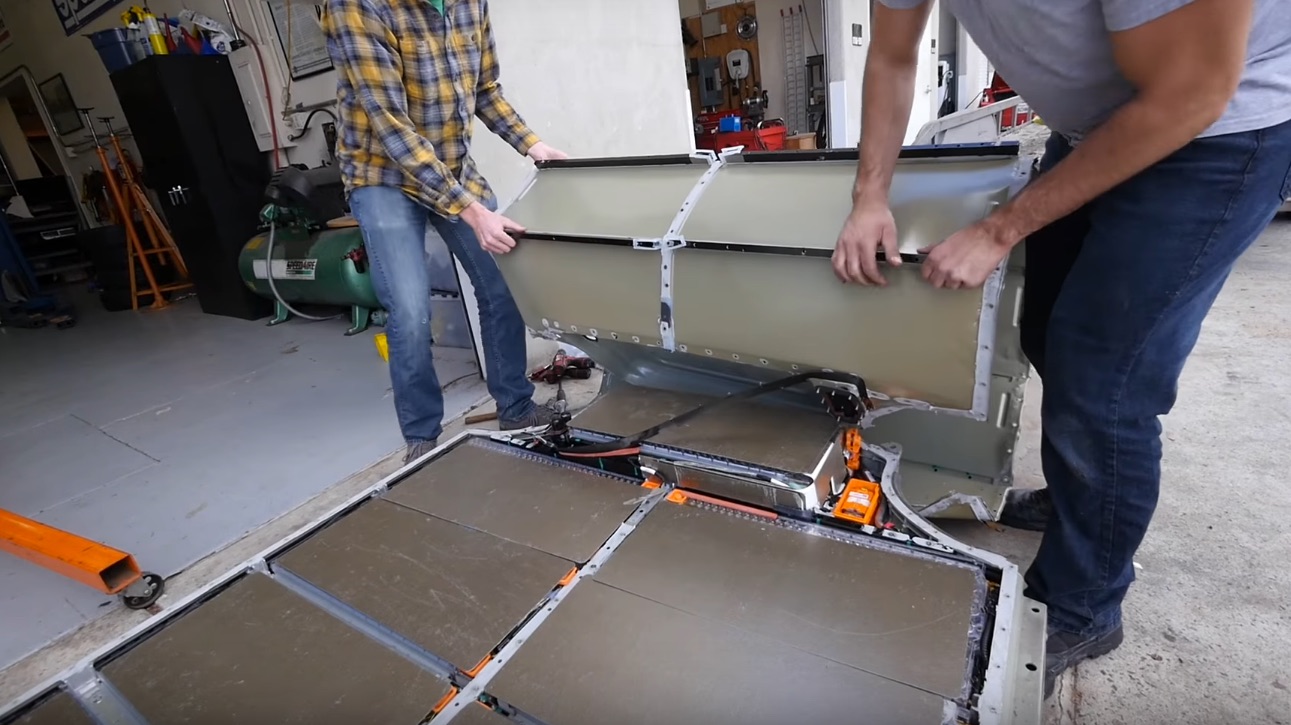
Tesla’s flex circuit technology could shake things up for companies that produce wiring and other electrical products.
A company specializing in wiring manufacturing called Lear Corporation was the target of bubbling doubts over how the flex circuit technology will impact future demand for wiring and cables.
During an earnings report, Chris McNally, an analyst from Evercore ISI, asked if flex circuits could “significantly reduce” wiring to the point where it would impact Lear’s business.
Frank Orsini, an executive at Lear Corp., didn’t seem fazed by the potential impact.
“The flex circuits and different types of applications in the vehicle is nothing new to Lear even. We’ve actually used flex circuits in the past. We have the technology in our product portfolio. It is more expensive technology than traditional applications of wire,” Orsini said. “What we do well in the industry is we optimize the architecture … We don’t see the usage of wire shrinking. Wires are very secured way of connecting the signaling and data communication in the vehicle.”
So while flex circuits could affect future wiring production, some company executives think that it doesn’t pose a major threat.
Flex circuits are basically a circuit system that can be molded and changed into different shapes. Overall, it drastically reduces the amount of cables and wiring needed when producing big electric-based projects like an EV.
Tesla patented a type of flexible circuit technology in 2013 for battery connection.
All the talk can be seen by Tesla fans as another way the company is pushing EV manufacturing into the future. Tesla has already had an impact on the auto market, with major automotive companies like BMW group and Volvo making the switch to electrified vehicles.
With flex circuits, the discussion can shift to how Tesla will impact production in the EV market as well. Based on CEO Elon Musk’s plans to vertically integrate all areas of vehicle production, implementing different wiring logistics could also impact how suppliers fit into the EV equation. Musk confirmed during Tesla’s first-quarter earnings call that the future Model Y compact SUV will utilize a new electrical system with significantly reduced wiring over previous models. This will enable faster manufacturing and an overall less complex design. Tesla’s flagship Model S and Model X have approximately 3 km of wiring within the vehicle, while Tesla’s highly anticipated Model 3 will have roughly half of that at 1.5km of wiring. Model Y, on the other hand, will only have 100m of wiring, a 95% reduction over Model 3.
As the Model 3 enters full-scale production, investors will get a chance to see just how big of an impact Tesla will have on EV manufacturing and the automotive industry as a whole.
Elon Musk
Tesla doubles down on Robotaxi launch date, putting a big bet on its timeline
Tesla continues to double down on its June goal to launch the Robotaxi ride-hailing platform.

Tesla has doubled down on its potential launch date for the Robotaxi ride-hailing platform, which will utilize the Cybercab and other vehicles in its lineup to offer driverless rides in Austin, Texas.
Tesla said earlier this year that it was in talks with the City of Austin to launch its first Robotaxi rides, and it planned to launch the platform in June.
This has been a widely discussed timeline in the community, with some confident in the company’s ability to offer it based on the progress of the Full Self-Driving suite.
However, others are skeptical of it based on Tesla’s history of meeting timelines, especially regarding its rollout of FSD.
Nevertheless, Tesla was asked when it would be able to offer Robotaxi rides and where, and it clearly is not backing down from that June date:
In Austin, 🔜
— Tesla (@Tesla) April 18, 2025
It is getting to a point where Tesla is showing incredible confidence regarding the rollout of the Robotaxi in June. We have not seen this kind of reiteration regarding the rollout of something regarding autonomy from Tesla at any point in the past.
CEO Elon Musk has even been increasingly confident that Tesla will meet its target. Earlier this week, he said the vehicles will be able to roll off production lines and drive themselves straight to a customer’s house:
Elon Musk continues to push optimistic goal for Tesla Full Self-Driving
There could be some discussion of an acceptable grace period, as the timeline for the Robotaxi rollout could still be considered a success, even if it were a month or two late. However, if it were pushed back further into 2025 or even 2026, skepticism regarding these timelines would continue to persist.
As of right now, it seems Tesla is extremely confident it will meet its goal.
Elon Musk
Tesla Semi fleet from Frito-Lay gets more charging at Bakersfield factory
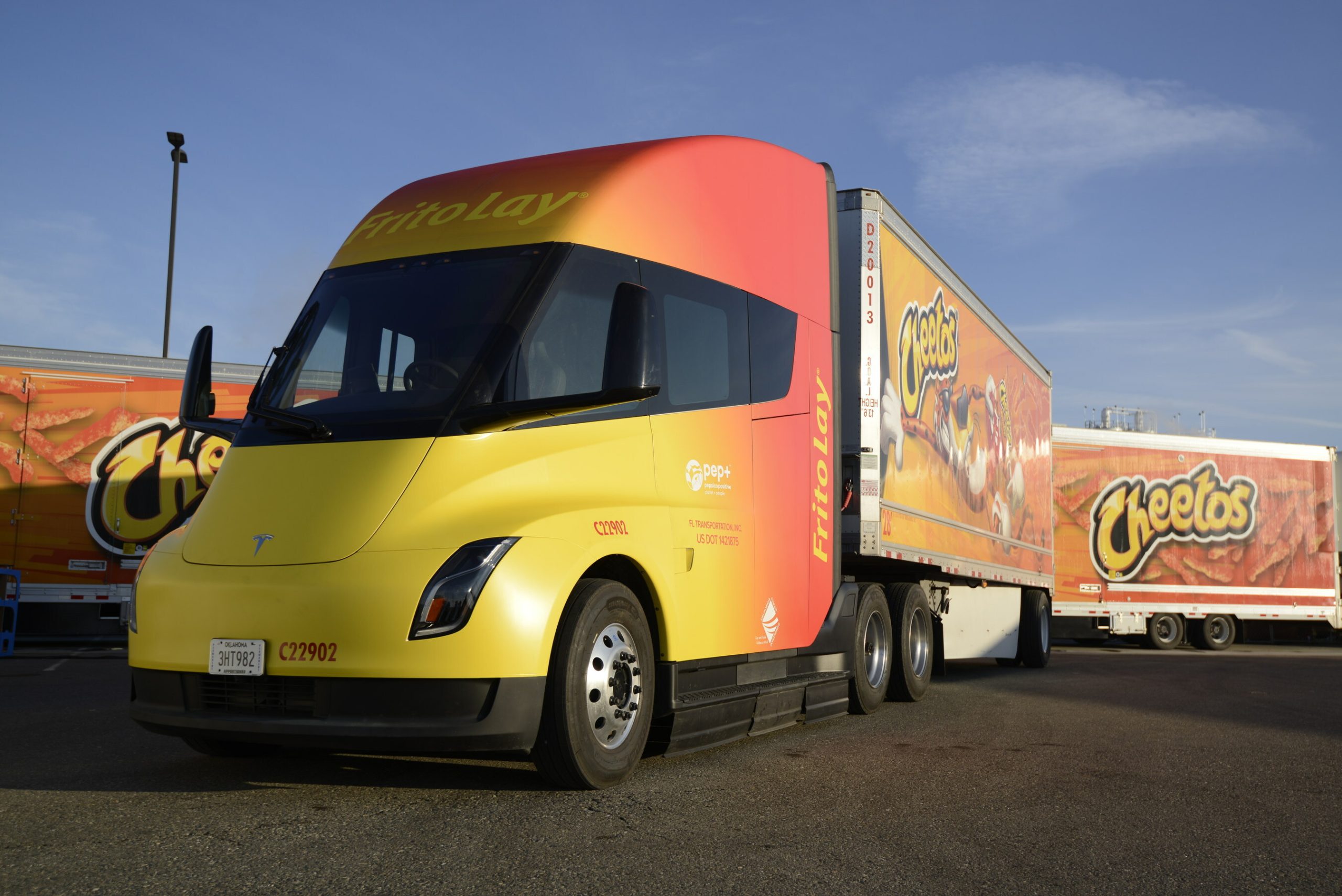

Among the several companies that have had the opportunity to add Tesla Semi all-electric Class 8 trucks to their fleets earlier than others, the most notable is arguably Frito-Lay, which has utilized the vehicle for a couple of years now.
However, as their fleet is making more local runs and there are undoubtedly plans to expand to more Semi units, the company has recognized it needs additional Megachargers to give juice to their trucks.
As a result, Frit-Lay decided to build more chargers at their Bakersfield, California facility, according to new permits filed by Tesla:
🚨 Frito-Lay is building an 8-stall Megacharger array at its factory in Bakersfield, California https://t.co/qARfJjogXF pic.twitter.com/gvorIVxsoc
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) April 18, 2025
There are already chargers at the company’s Modesto, California, factory, but Bakersfield is roughly three hours south of Modesto.
Interestingly, Tesla is calling the chargers “Semi Chargers” in the filing, potentially hinting that it is no longer referring to them as “Megachargers,” as they have been in the past. This is a relatively minor detail, but it is worth taking note of.
In 2022, Frito-Lay began installing these chargers in preparation for the Semi to become one of the company’s main logistics tools for deliveries in California and surrounding states.
Frito-Lay is not the only company that has chosen to utilize the Tesla Semi for these early “pilot” runs. PepsiCo has also been a company that has used the Semi very publicly over the past two years.
Additionally, the Tesla Semi participated in the Run on Less EV trucking study back in late 2023, where it managed to complete a 1,000-mile run in a single day:
Tesla Semi logs 1,000-mile day in Run on Less EV trucking study
Tesla is planning to ramp production of the Semi late this year. On the Q4 2024 Earnings Call, VP of Vehicle Engineering Lars Moravy said the company would be focusing on the first builds of the Semi’s high-volume design late this year before ramping production in the early portion of 2026:
“We just closed out the Semi factory roof and walls last week in Reno, a schedule which is great with the weather. In Reno, you never know what’s going to happen. But we’re prepping for mechanical installation of all the equipment in the coming months. The first builds of the high-volume Semi design will come late this year in 2025 and begin ramping early in 2026.”
Tesla will build these units at a new Semi production facility located in Reno near its Gigafactory. The company is getting closer to finishing construction, as a drone video from this morning showed the facility is coming along at a good pace:
🚨Tesla Semi factory progress update: pic.twitter.com/dlzIjKwfT3
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) April 18, 2025
News
Tesla Cybercab no longer using chase vehicles in Giga Texas
Elon Musk expects Tesla to produce about 2 million Cybercab units per year.
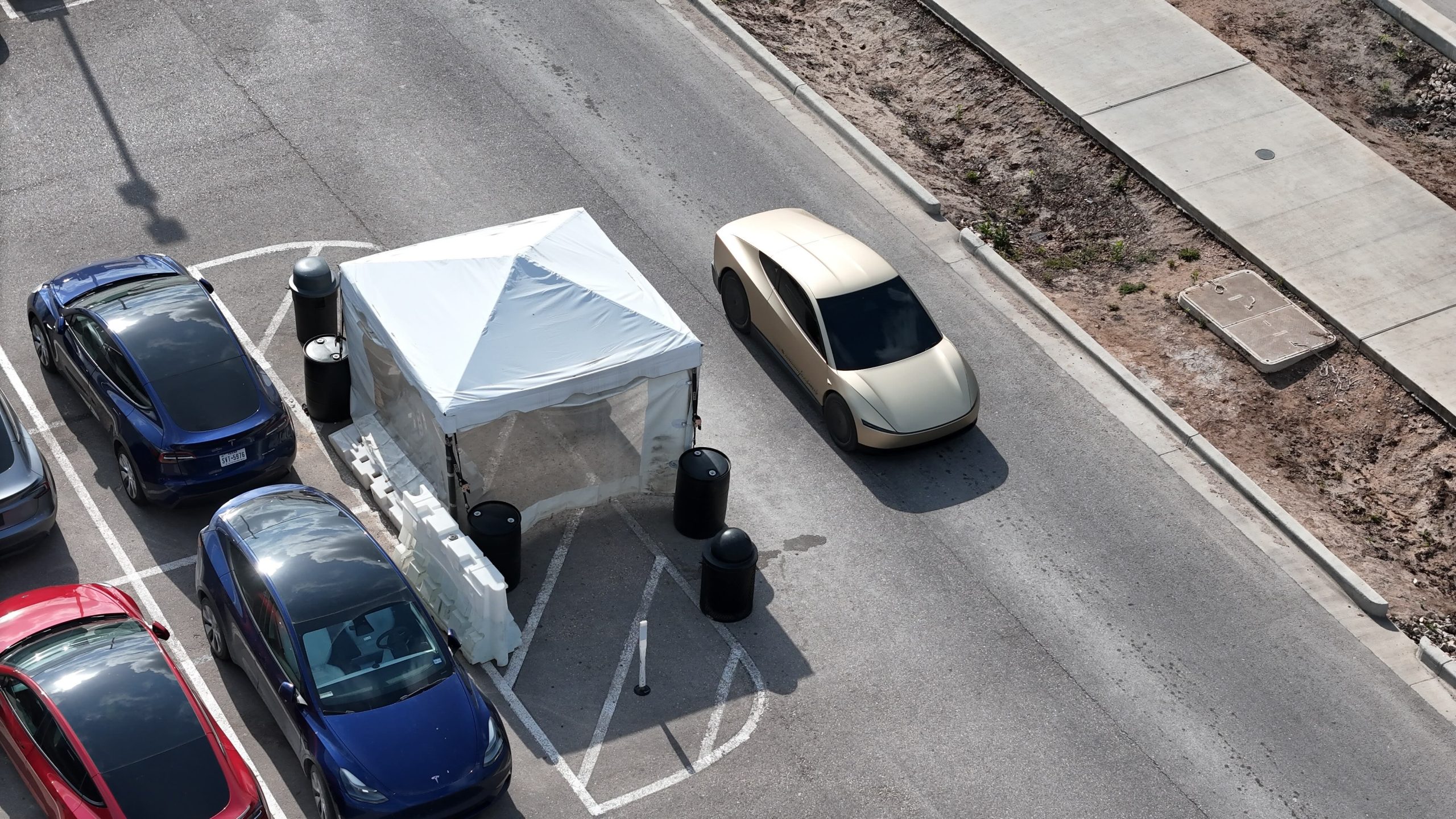

The Tesla Cybercab is the company’s first vehicle that is designed solely for autonomous driving. And while the spacious two-seater is expected to start volume production in 2026, the vehicle’s development seems to be moving at a steady pace.
This was hinted at in recent images taken by a longtime Tesla watcher at the Giga Texas complex.
Tesla Cybercab Production
The Cybercab will likely be Tesla’s highest volume vehicle, with CEO Elon Musk stating during the company’s Q1 2025 All-Hands meeting that the robotaxi’s production line will resemble a high-speed consumer electronics line. Part of this is due to Tesla’s unboxed process, which should make the Cybercab easy to produce.
Elon Musk expects Tesla to produce about 2 million Cybercabs per year. And while the vehicle is expected to see volume production at Giga Texas next year, the CEO noted that the vehicle will be manufactured in more than one facility when it is fully ramped.
No More Chase Cars
While the Cybercab is not yet being produced, Tesla is evidently busy testing the vehicle’s fully autonomous driving system. This could be hinted at by the Cybercabs that have been spotted around the Giga Texas complex over the past months. Following last year’s We, Robot event, drone operators such as longtime Tesla watcher Joe Tegtmeyer have spotted Cybercabs being tested around the Giga Texas complex.
At the time, videos from Giga Texas showed that the driverless Cybercabs were always accompanied by a manually driven Model 3 validation chase car. This was understandable considering that the Giga Texas complex features pedestrians, other cars, and construction areas. As per the drone operator in a recent post on social media platform X, however, Tesla seems to have stopped using chase cars for its Cybercab tests a few weeks ago.
Aggressive Tints
The reasons behind this alleged update are up for speculation, though it would not be surprising if the Cybercab’s autonomous driving system could now safely navigate the Gigafactory Texas complex on its own. Interestingly enough, the Cybercabs that were recently photographed by the drone operator featured very aggressive tint, making it almost impossible to make out the interior of the robotaxi.
This is quite interesting as other Cybercabs that have been spotted around Giga Texas were only equipped with semi-dark tints. One such vehicle that was spotted in February was even speculated to be fitted with an apparent steering wheel.
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla rolls out new, more affordable trim of the Model Y Juniper in U.S.
-
 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla expands Early Access Program (EAP) for early Full Self-Driving testing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla celebrates key milestone for 4680 battery cell production cost
-

 Investor's Corner2 weeks ago
Investor's Corner2 weeks ago“Nothing Magnificent about Tesla (TSLA),” claims Jim Cramer
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoI took a Tesla new Model Y Demo Drive – Here’s what I learned
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Europe shares FSD test video weeks ahead of launch target
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoThis Tesla executive is leaving the company after over 12 years
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Giga Texas vehicles now drive themselves to outbound lot





















