News
SpaceX to demonstrate weekly launch cadence: 3 launches in 14 days

LC-39A undergoing repairs and tests after the launch of CRS-11. (/r/SpaceX)
SpaceX is in the process of preparing to launch BulgariaSat-1, with the first attempt scheduled for Saturday, June 17th between 2:10 p.m and 4:10 p.m. EST. BulgariaSat-1 will be Bulgaria’s second satellite ever and will act as a telecommunications hub in geostationary orbit, around 30,000 miles above Earth.
Following a highly successful launch and docking of the eleventh cargo mission of its Dragon spacecraft, Launch Complex 39A has since undergone routine checks to verify its condition and has likely been lightly repaired. The static fire for the upcoming mission is scheduled as early as tomorrow. Both the static fire and launch were pushed back two days due to a 48 hour delay of the CRS-11 launch.
The launch of BulgariaSat-1 is already exceptional for several reasons. First and foremost, the Falcon 9 first stage to be used in the upcoming mission has already flown once before, assisting in the successful launch of Iridium’s first ten NEXT satellites in early January of this year. It will thus mark the second time SpaceX has truly reused a Falcon 9 first stage. There has even been a bit of circumstantial evidence that the choice to launch on a recovered F9 resulted in BulgariaSat-1 being moved ahead of Intelsat 35e, which is now scheduled for no earlier than July 1st. Regardless, another successful reuse will be a boon for a SpaceX in the throes of an unprecedentedly busy year of launches by once again demonstrating the viability of their program of reuse and thus hopefully swaying more customers to take the leap to reused rocket cores.
The second reason, as touched on above, is that BulgariaSat-1 will mark the beginning of a two week period in which SpaceX could potentially conduct three separate launches, two at Cape Canaveral and one at Vandenberg Air Force Base. If successful, this would demonstrate weekly single-vehicle launch cadence, something that has not been seen in the launch industry in quite some time. This weekly cadence, if successful, will demonstrate a maturing company that is truly preparing for extraordinary launch cadence. By using two pads, one in California and one in Florida, SpaceX will still be able to provide two weeks between launches in order to prepare each launch site for the next launch, while effectively launching once a week. While Vandenberg Air Force Base can only support polar orbit launches, LC-40 is currently deep into the process of being repaired and reactivated following the failure of a Falcon 9 late last year.
With LC-40 preparing for reactivation sometime in August or September, SpaceX will find themselves at long last with two viable all-purpose launch pads in very close proximity to each other. By staggering launches on each pad and continuing to maintain the two week pad turnaround time after launches, SpaceX could theoretically begin to sustain regular weekly launches as few as three months from now. A successful weekly cadence this month could reinforce that such a sequence of events is a possibility.

Iridium NEXT 1’s Falcon 9 first stage after recovery in the Pacific Ocean. (SpaceX)
SpaceX has long been working to rapidly increase its ability to launch frequently, and this year has been an exceptional example of several pieces fitting together. The company has begun to use an automated flight termination system, which will allow them to rely less upon the availability of Cape Canaveral’s Range Officers while crafting their manifest and launch schedules. Normally, the flight termination system in rockets is monitored by an actual team of people who have barely a few seconds to decide if rocket telemetry is less than nominal and prevent what is effectively a large missile from impacting populated areas. SpaceX has replaced this with an arguably much safer approach dependent upon their mature autonomous avionics systems, simply meaning that computers on board their rockets and spacecraft automatically analyze telemetry and control vehicle performance and guidance. SpaceX has been testing this system in a way that is almost identical to Tesla’s method of installing inert autonomy software that can learn without actually controlling the vehicle, and it is consequently only now being implemented after SpaceX and the Air Force have a high degree of confidence that it will outperform its human colleagues.
The ultimate goal of this automated flight termination system (AFTS), as well as many other significant changes to both the hardware of pads and vehicles, is to eventually allow SpaceX to accomplish Elon Musk’s long fabled and oft-ridiculed goal of 24-hour reusability, and thus 24-hour launch cadence. SpaceX and the USAF have both stated that AFTS alone will likely allow Cape Canaveral to support up to 48 launches a year. While shared between ULA and SpaceX, even 36 launches a year would effectively leave SpaceX with a shrinking launch manifest and significantly increased revenue and profit. This would speculatively allow them to more rapidly develop their pursuits of Mars, a vast constellation of broadband satellites, and more.

BulgariaSat-1 being prepared for launch. (SSL)
Nevertheless, this is all of course speculation and dependent upon many things going well. If SpaceX is able to successfully launch BulgariaSat-1 on June 17th, Iridium NEXT 2 on the 25th, and Intelsat 35e on July 1st, they will have successfully demonstrated the ability to support a weekly launch cadence and will have to do little more than wait for the availability of a second East coast pad to begin to take full advantage of it.
With ten launches scheduled between now and October and ten more launches scheduled between October and the end of December, it is guaranteed to be one incredible year for SpaceX and their fans.

News
Waymo, Uber launch driverless ride-hailing in Austin
The commercial robotaxi industry is heating up.
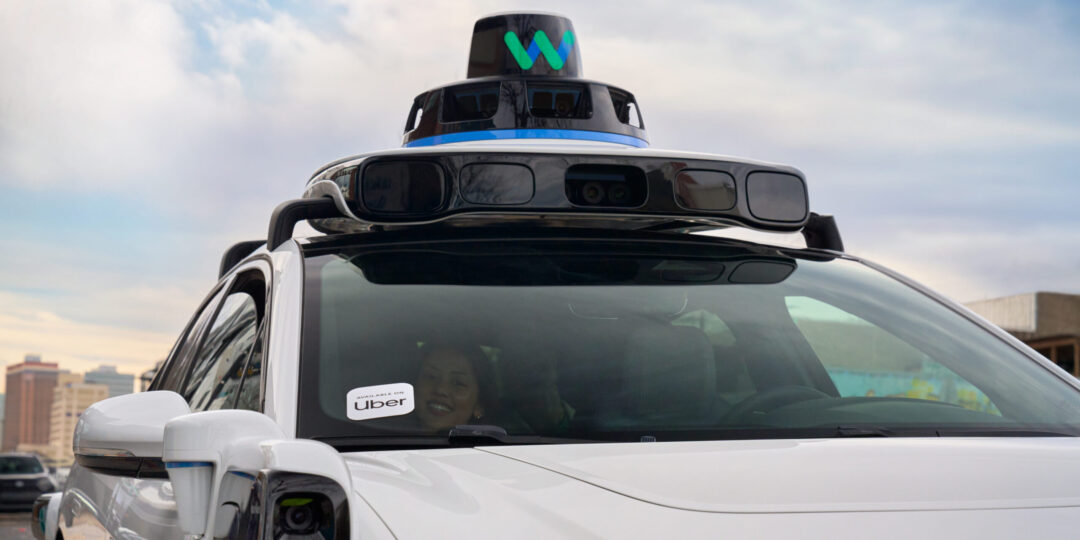

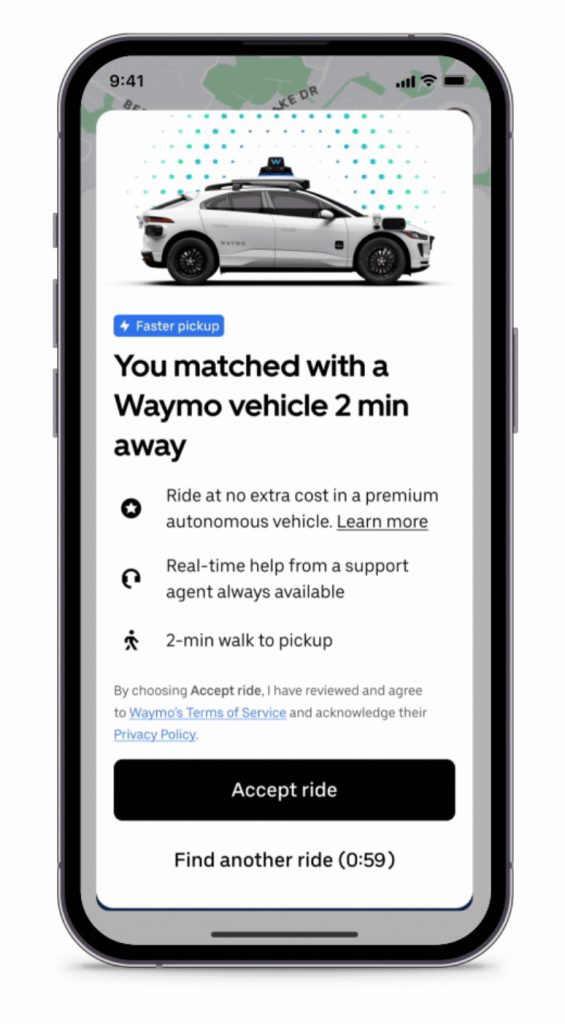
As the emerging commercial robotaxi space grows with Tesla and others set to start deploying self-driving ride-hailing services, Waymo, the robotaxi firm owned by Google parent company Alphabet, has officially launched driverless taxis in Texas, with the help of Uber.
As of Tuesday, those in Austin can officially take a driverless Waymo robotaxi using the Uber app, as detailed in a press release from the ride-hailing company. The launch comes as Tesla is expected to debut Unsupervised Full Self-Driving (FSD) services in Austin later this year, and after it was found to have applied for a permit to operate ride-hailing vehicles in California.
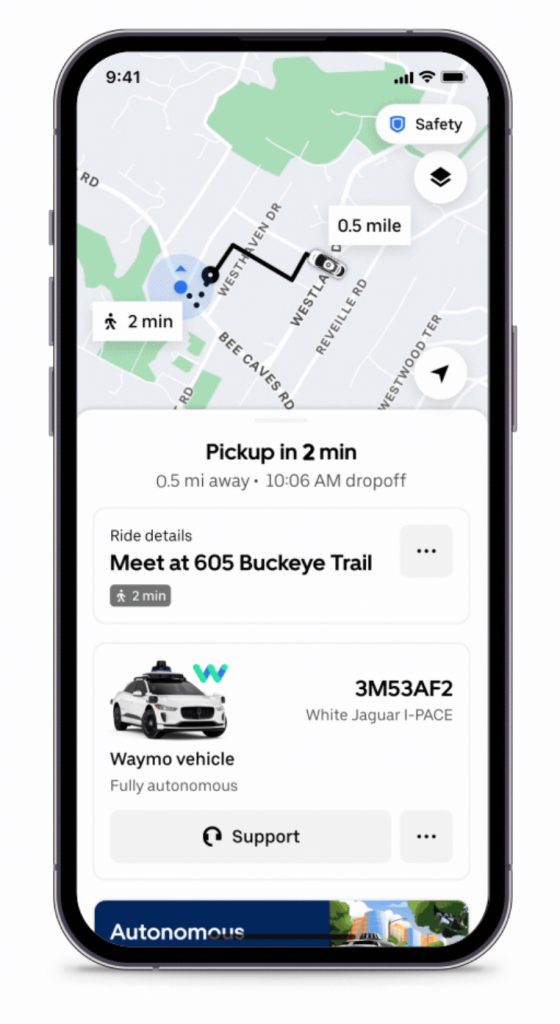
To access the Waymo robotaxis, users must opt in for the service on the Uber app at no additional cost. When awaiting rides, riders will have the option to accept the driverless Waymo robotaxi or to switch to a non-self-driving vehicle instead.
Additionally, riders will be able to use the Uber app to unlock the vehicle, open the trunk, and activate the trip, and the ride-hailing company also says it’s providing 24/7 customer support in case of any issues. The area of operation will allow riders to travel across 37 square miles of Austin, from Hyde Park to Downtown to Montopolis, and Uber also says the company plans to expand the service area in the future.
The launch also comes ahead of the South by Southwest (SXSW) music festival in Austin this weekend, which is expected to bring in bands and music enthusiasts from all over the world.
- Credit: Uber
- Credit: Uber
READ MORE ON ROBOTAXIS, TESLA’S FSD:
- Tesla is going in-house for robotaxi platform, says one competitor
- Tesla China owners share first impressions of FSD-style ‘City Autopilot’
- Tesla used this clever workaround to train FSD for China’s roads
- Tesla FSD’s rollout in Mexico is a bigger deal than it seems
- Cruise layoffs begin as GM winds down robotaxi business
- Waymo to test self-driving vehicles in another country in 2025
- Waymo study analyzes collisions with vulnerable road users
Waymo currently operates paid, self-driving ride-hails via an in-house platform through the Waymo One app in Los Angeles and around San Francisco, California, as well as in Phoenix, Arizona. As part of the announcement, Uber also says that the two companies will be partnering to launch robotaxi services in Atlanta, Georgia next.
During Tesla’s Q4 earnings call in January, CEO Elon Musk said that Tesla plans to launch its Unsupervised FSD system as a paid service in Austin in June. Tesla also operates a Gigafactory in Austin, where it builds the Model Y and the Cybertruck, and Musk has said launching in the city would let the company “dip its toe in the water” of commercial robotaxis with safety in mind.
In October, Musk also said that Tesla had been testing internal ride-hails for employees in the Bay Area, California, adding that users could already request a ride and be dropped off anywhere in the Bay. Last week, it was also widely reported that Tesla had in November applied for a “transportation charter-party carrier permit” from the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC), which is the agency that helps regulate the state’s autonomous vehicles.
Tesla also launched its two-seat, steering wheel-less Cybercab in October during a Southern California event dubbed “We, Robot,” and you can see our coverage from the event below.
🎥: Our FULL first ride in the @Tesla Cybercab pic.twitter.com/6gR7OgKRCz — TESLARATI (@Teslarati) October 11, 2024
Tesla mobile app tracker reports first lines referencing robotaxi service
News
Rivian teams up with Ben & Jerry’s on an electric ice cream truck
The age-old ice cream truck gets some new electric digs.
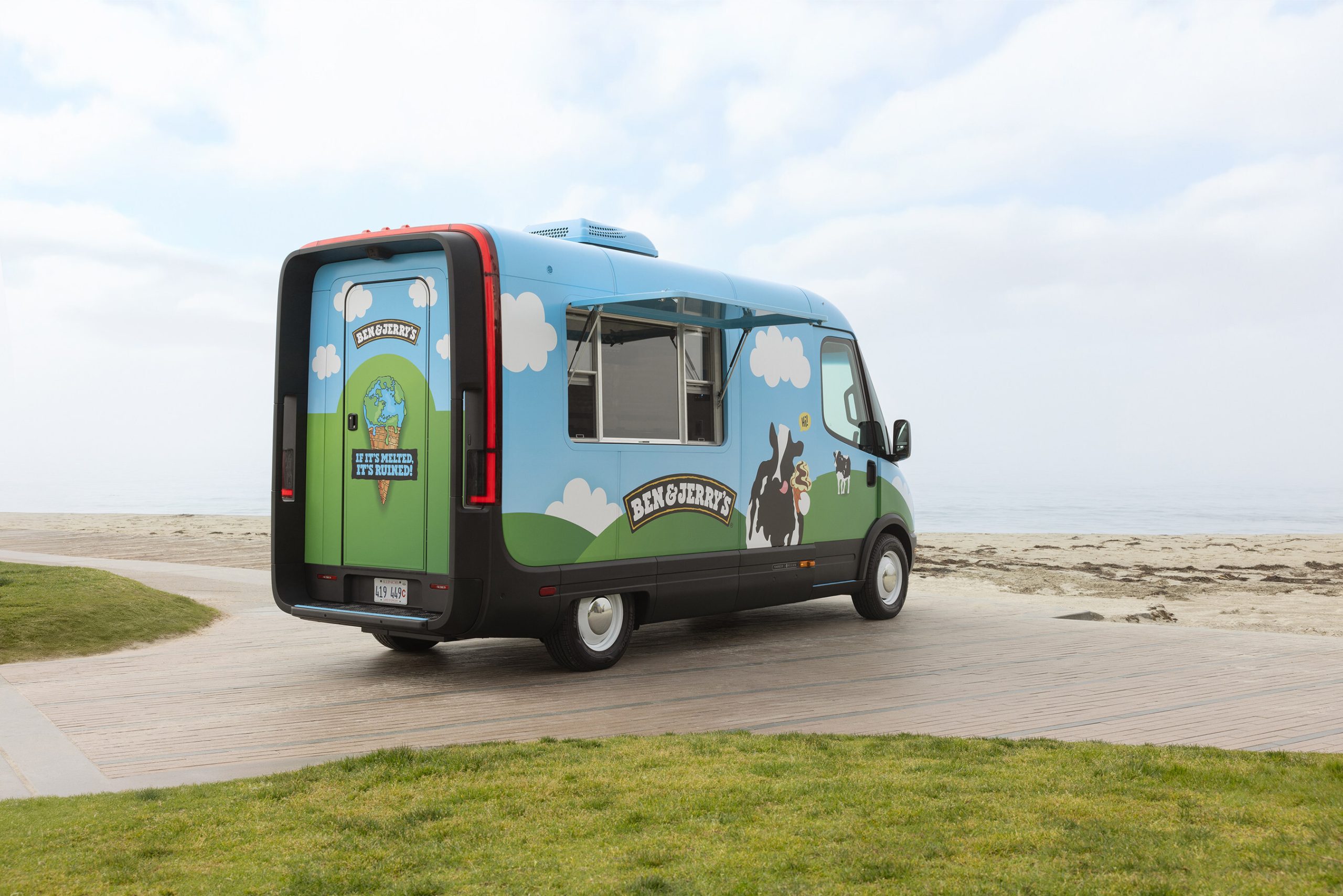

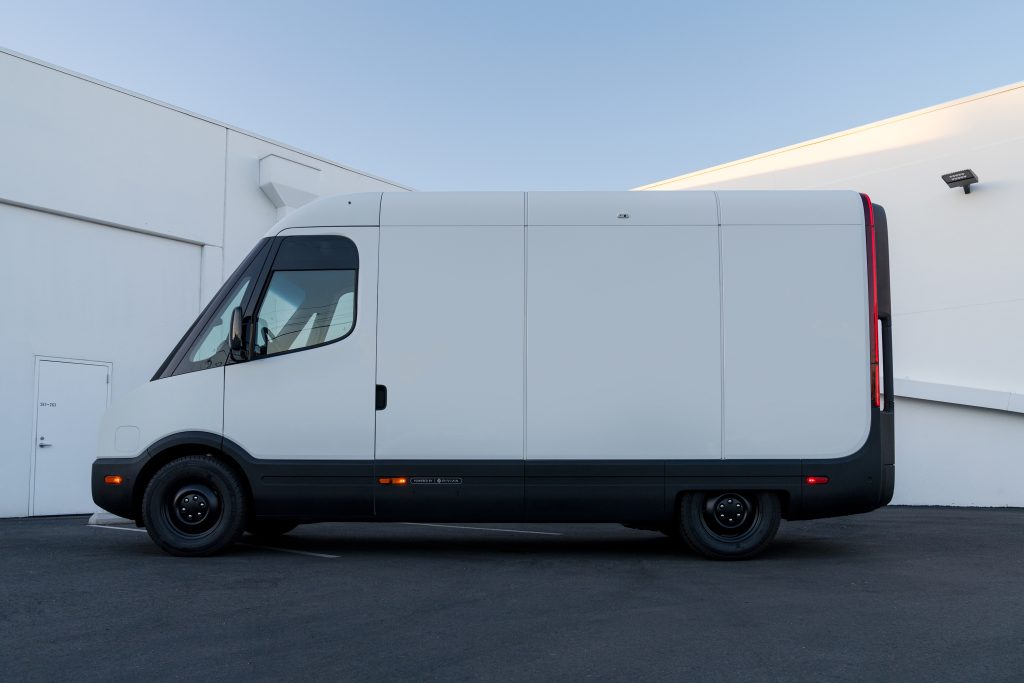
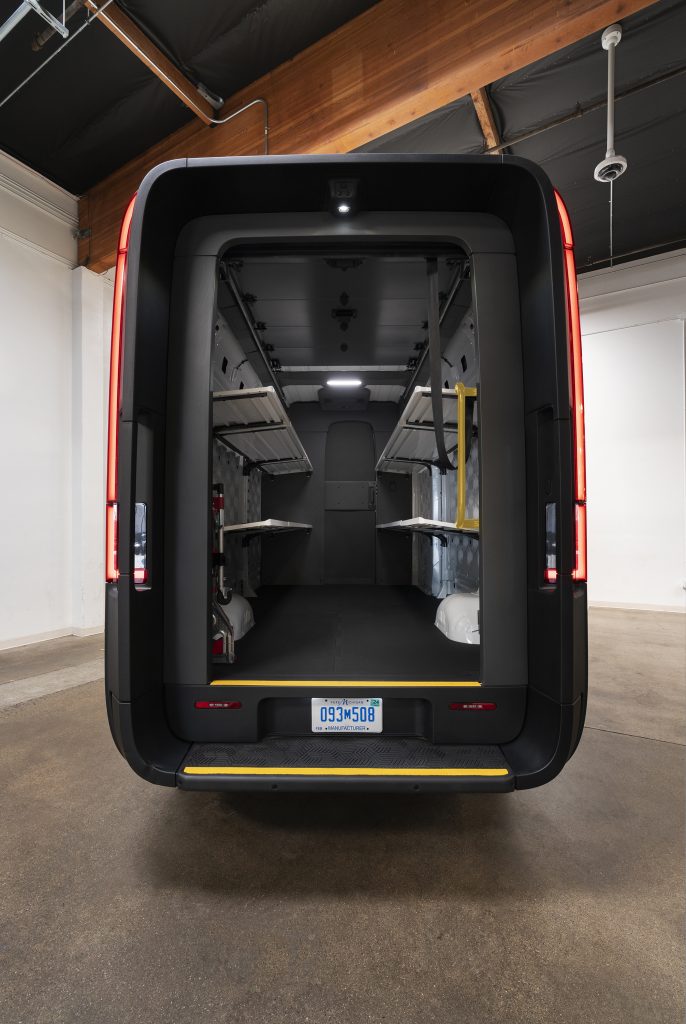
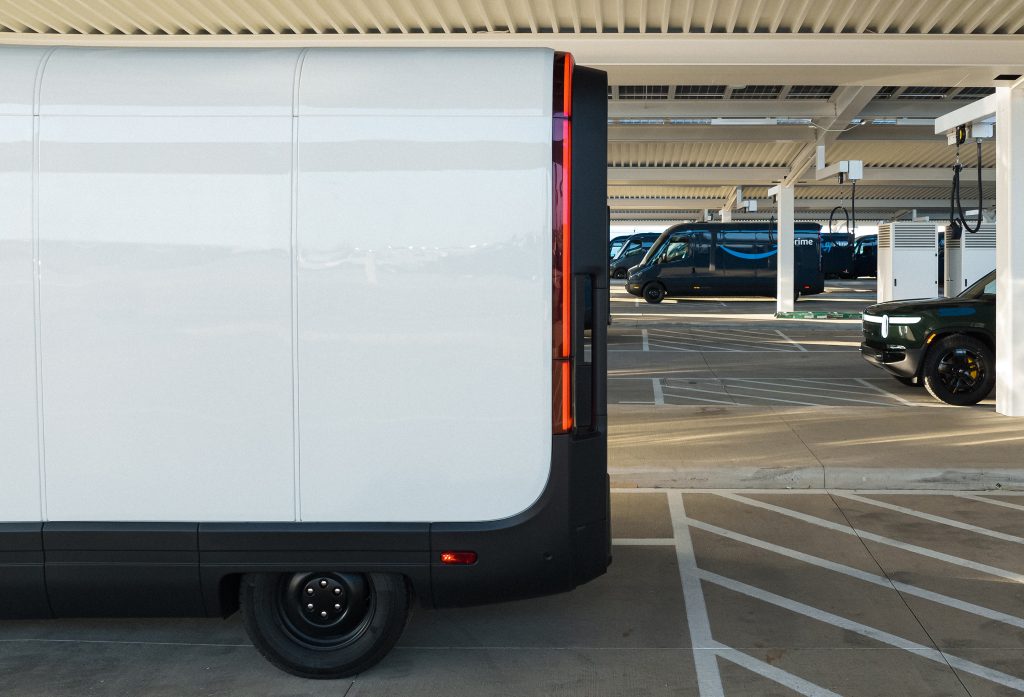
Rivian has officially teamed up with the ice cream company Ben & Jerry’s to launch an electrified ice cream truck, weeks after the electric vehicle (EV) maker launched its van to more commercial customers.
As detailed in a press release on Tuesday, Rivian and Ben & Jerry’s have unveiled two “Scoop Trucks,” a pair of electric ice cream trucks based on the Rivian Commercial Van (RCV). Rivian officially launched the RCV to commercial customers beyond its early partner Amazon last month, and the Scoop Truck is one of the first we’ve seen of its modular use cases in the weeks since.
The companies plan to debut the first of the electric ice cream trucks at the South by Southwest (SXSW) music festival in Austin, Texas, which starts on Friday. After the festival, both of the Scoop Trucks will be hitting the road across the U.S., along with joining a series of pop-up events in Vermont, where Ben & Jerry’s is headquartered.

Credit: Ben & Jerry’s

Credit: Ben & Jerry’s
“Collaborating with the Ben & Jerry’s team to build the next generation of electric scoop trucks has been an incredible experience. It’s one of those projects that just makes the team smile,” said Brian Gase, Rivian’s Senior Director of Prototype Development. “We can’t wait for people to stop by for some ice cream and see it in action for the first time during SXSW!”
The Scoop Trucks appear to be the Rivian RCV 500, offering a 161-mile range, and an overall length of 248.5 inches. The electric van also includes a 100 kWh LFP battery pack, and Rivian says it can charge at speeds of up to 100 kW.
“Working with Rivian, an industry leader that is committed to sustainability is an ice cream dream come true,” notes Sean Slattery, Ben & Jerry’s U.S. Integrated Marketing project lead. “Today, Rivian helped Ben & Jerry’s reduce our reliance on fossil fuels in a small way, while making things a little bit cooler… which, as an ice cream company, is extremely difficult to do.”
A photo of one of the Rivian Scoop Trucks was also spotted and photographed being hauled in Irvine, California, as was shared on Reddit last week. As one viewer points out, the RCVs include an extra air conditioning unit on top of the van, in order to help keep necessary refrigeration running.
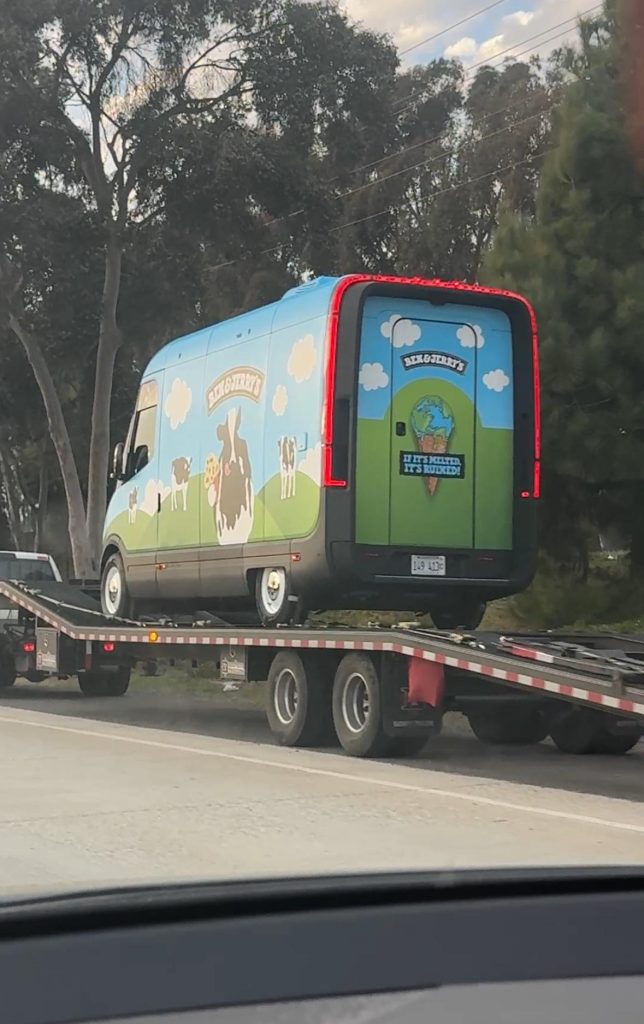

Credit: riceengineer | Reddit

Credit: Rivian

Credit: Rivian

Credit: Rivian
READ MORE ABOUT RIVIAN: Rivian releases its Q4 and full-year 2024 financial results
Along with the Ben & Jerry’s RCV, Rivian is partnering with SXSW on an “Electric Roadhouse” exhibit, which will include panel discussions, demo drives, live music, and even a look at the upcoming R2 line. Rivian is also set to be an official sponsor for the music festival’s Transportation Track event. The Scoop Truck is likely to play a role in the upcoming Rivian event, though the companies have yet to disclose where exactly it can be seen this weekend.
In December, Rivian announced that it has deployed 20,000 of the Electric Delivery Vans (EDVs), which are the Amazon-exclusive launch version of the RCVs. Produced alongside the R1T and R1S at the company’s factory in Normal, Illinois, the vans come in two configurations, the RCV 500 and the longer RCV 700, which are both currently being offered for fleet sales.
Rivian is also aiming to build a factory in Georgia with help from a $6.6 billion loan from the Department of Energy (DOE), though these plans are up in the air under the Trump administration’s recent freeze on federal grants and loans. CEO RJ Scaringe in January said that the automaker has already signed a “legally binding agreement” with the DOE, featuring a broad range of conditions that Rivian must meet along the way.
News
Tesla launches fresh U.S. promotions for the Model 3
With the end of Q1 now just weeks away, Tesla has launched two different promos on the Model 3.

Tesla has launched fresh incentives for the Model 3 sedan, coming as the automaker aims to ramp up deliveries as part of its end-of-quarter push.
With just a few weeks left in the first quarter of year, Tesla is now offering three separate incentives for all Model 3 trims in the U.S., including zero-percent APR financing, $0 due at signing, and 60-month terms. The promos were announced on social media and they’re currently also detailed on the company’s order configurator for the electric vehicle (EV).
Credit: Tesla
Tesla North America announces a new set of incentives for the reengineered Model 3 sedan.🇺🇸
✅0% APR for all Model 3 trims
✅$0 due at signing
✅60 month termsNot bad at all for one of the best bang-for-the-buck vehicles, electric or otherwise, in the market today. pic.twitter.com/3vM7Ioo2lV
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 4, 2025
To qualify for the zero-percent APR deal in the U.S., buyers must put a down payment of at least 15 percent down, though Tesla also says the federal tax credit can go toward this if eligible. The $0 due at signing deal comes at a 0.99 percent APR with the use of the tax credit, and both of the deals come with 60-month terms.
At the time of writing, the $7,500 federal tax credit is also still available for all three Model 3 trims, amidst some speculation around whether or not the Trump administration could do away with the government incentive. Tesla’s website does not currently show the incentive on the order configurator in Canada, though the company is still offering a 0.99-percent APR deal on orders placed before March 7. On the Mexico order configurator, neither of these promotions are currently available.
It’s common for Tesla to push additional promos at the end of each quarter, and especially at the end of the year, to try to boost delivery numbers that will be included with quarterly data. The news also comes after Tesla began deliveries of the Model Y refresh in the U.S. earlier this week, after first deliveries of the Gigafactory Shanghai-built SUV started going out last week.
Tesla originally launched the refreshed Model 3 last January, a few months after the redesigned sedan became available in the Asia-Pacific and Europe-Middle East markets. Not unlike the recently launched Model Y, the Model 3 “Highland” came with a number of interior and exterior upgrades in two configurations, before Tesla launched the highly-anticipated Performance trim in May.
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoTesla mulls adding a new feature to fight off vandals as anti-Musk protests increase
-

 News9 hours ago
News9 hours agoTesla launches fresh U.S. promotions for the Model 3
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoTesla’s lead designer weighs in on plans for these two Model Y colors
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoTesla starts Model Y ‘Launch Edition’ deliveries in the U.S.
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoTesla design head reflects on over 16 years with the company
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoTesla gaining with Republicans as it loses traction with Democrats: Stifel
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoTesla launches 100+ Supercharger partnership with this fast food chain
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoAnti Elon Musk protester attacks Polestar after mistaking it for a Tesla