
SpaceX
SpaceX’s Mr. Steven highlights ambiguity of Falcon fairing catches with port return
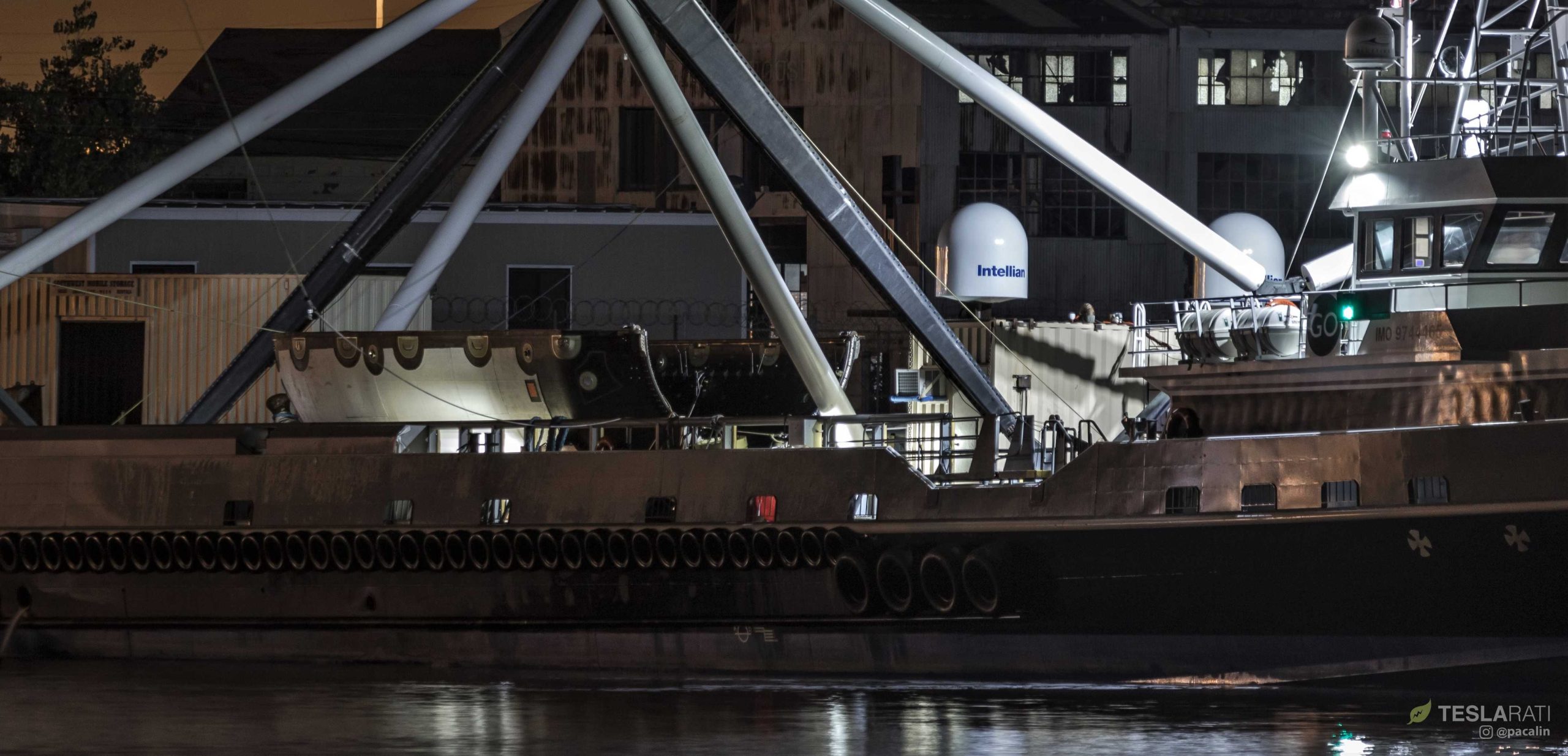
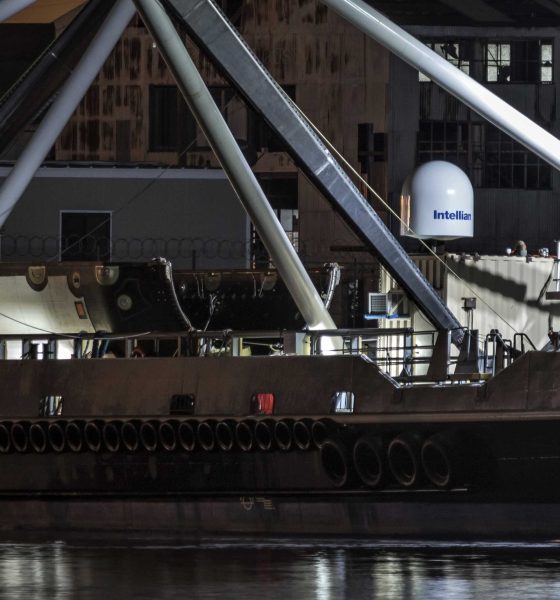
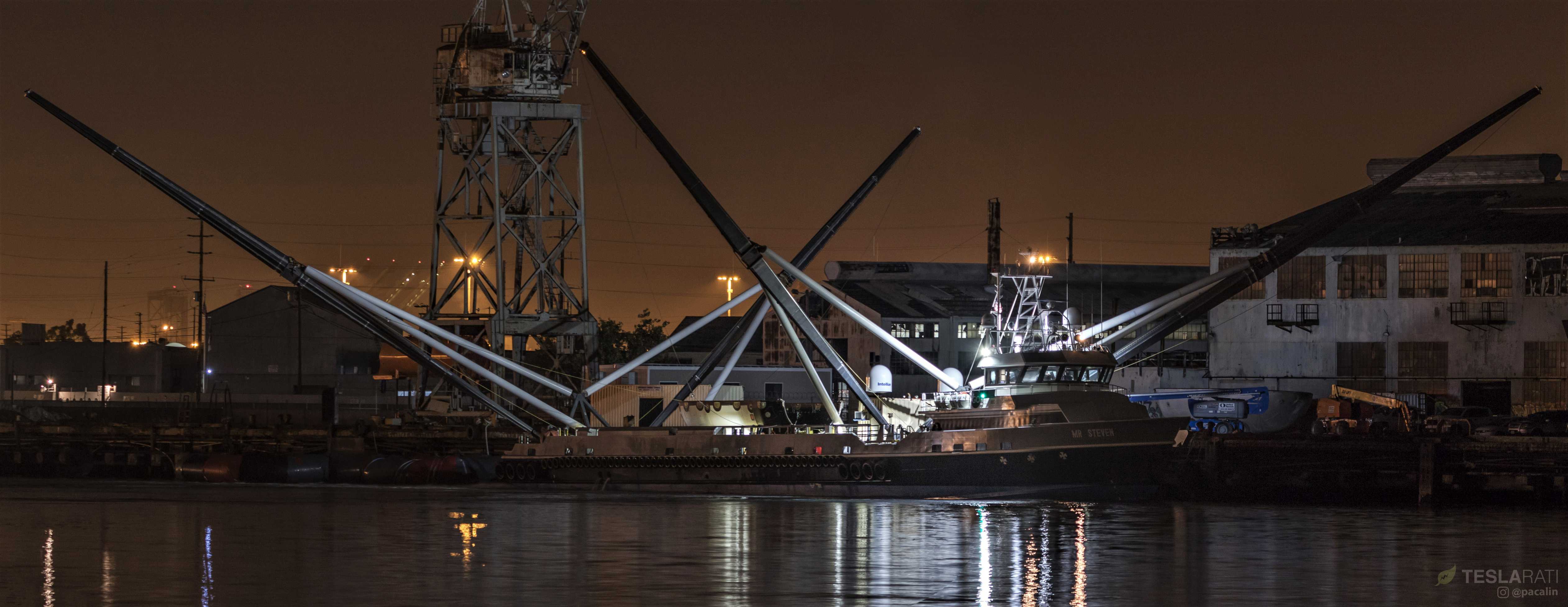
SpaceX’s fairing recovery vessel Mr. Steven highlighted the maddening and exhilarating uncertainty of unpublicized fairing recovery attempts with a return to Port of San Pedro on October 18th, the morning after spending a day at sea for the second Falcon fairing drop-and-catch test.
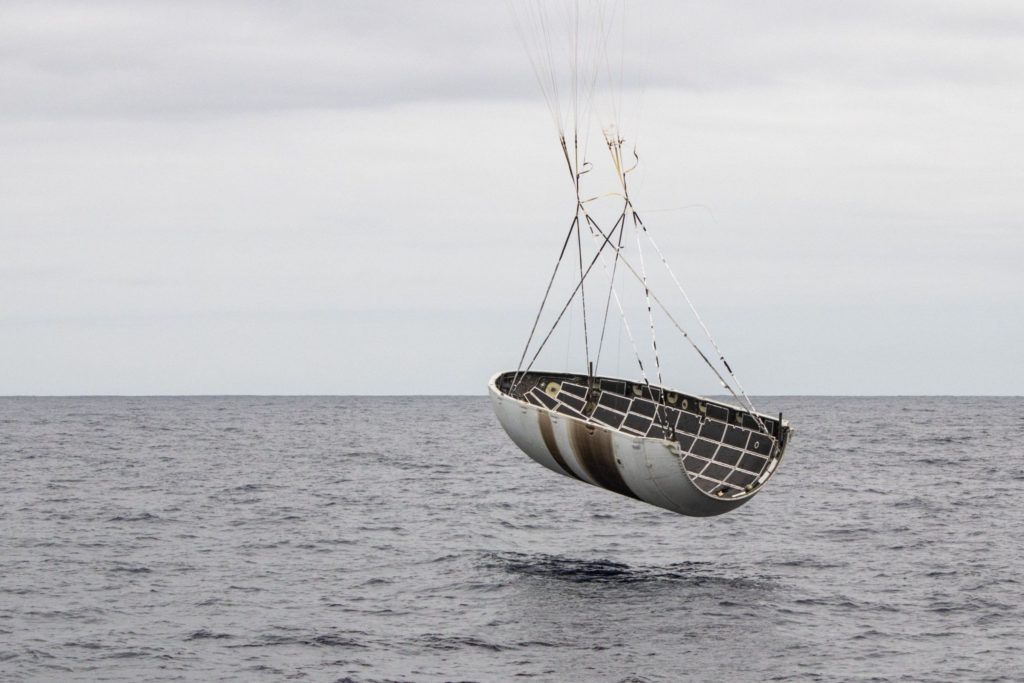
Teslarati photographer Pauline Acalin was on site to watch Mr. Steven’s 1AM Pacific port return and was able to capture the arrival, showing a familiar test fairing resting on the vessel’s deck, perfectly intact, with the recovery net fully retracted.

Schrödinger’s Fairing
Beginning with a dry run on October 8th, SpaceX technicians and engineers have spent the last 10 days testing Mr. Steven more intensely than ever previously observed, centering around a campaign of apparent Falcon fairing drop tests. Although it’s possible that these tests are more captive-carry trials than true drop tests, it seems more likely – judging by the fact that NOTAMs, notices to airmen, were only filed for 2 of the 3 attempts – that the helicopter is actually releasing a fairing half around 11,000 feet (3300 m) and letting it glide towards Mr. Steven.
Previously, SpaceX executive Hans Koenigsmann and CEO Elon Musk have mentioned a probable drop test campaign if operational (post-launch) fairing recovery attempts were unsuccessful. Mr. Steven has yet to successfully snag a fairing out of the air over the course of four post-launch catch attempts, evidence that – just like landing Falcon 9 boosters intact – recovering orbital-class rocket hardware in a state that allows for future reuse is extraordinarily difficult, regardless of the subsystem. However, SpaceX has managed to successfully recover fairing halves intact and in a condition good enough to make Koenigsmann, Vice President of Reliability, visibly excited during an IAC 2018 presentation.
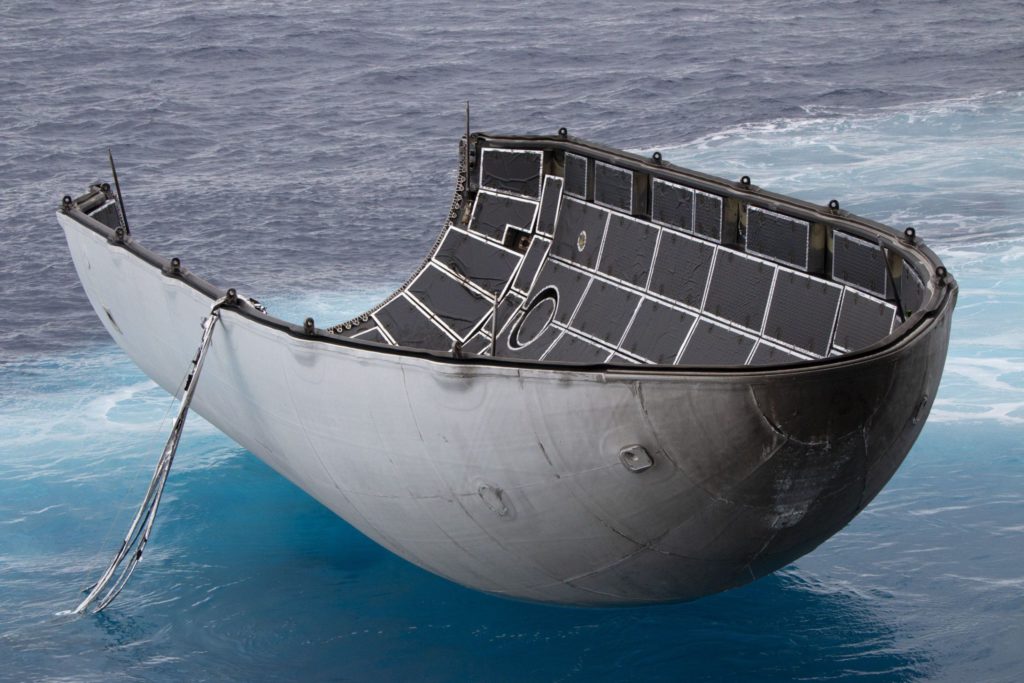
- Hans Koenigsmann was extremely excited about the condition of this particular fairing half, and included this photo in his IAC 2018 keynote. (SpaceX)
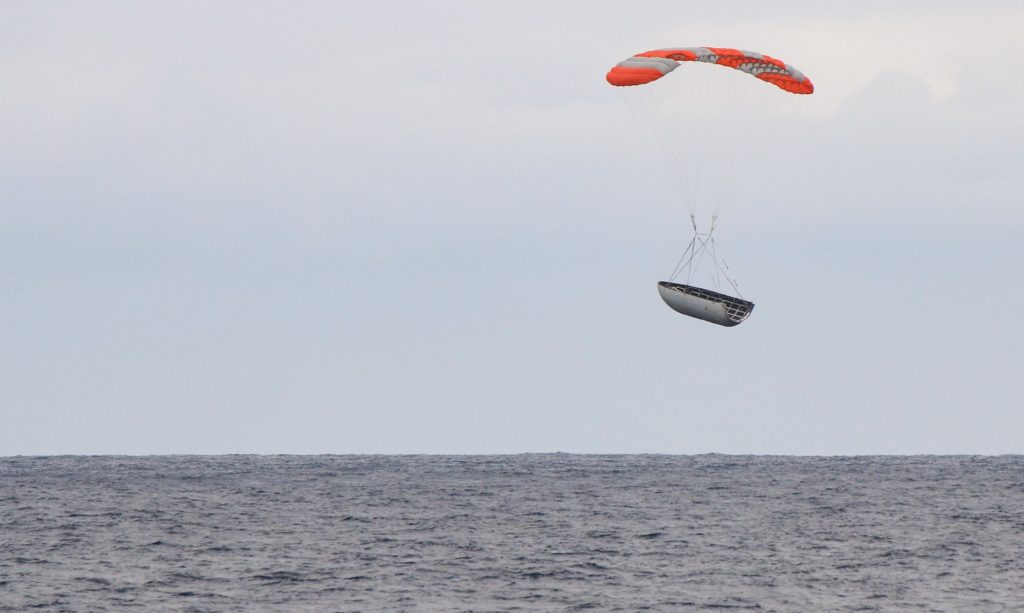
- One half of SpaceX’s Iridium-6/GRACE-FO just moments before touchdown on the Pacific Ocean. (SpaceX)
- Close. (SpaceX)
The problem with those intact halves is that they have been recovered only after soft landings in the ocean – once immersed in saltwater, the sheer expense of cleaning a fairing to the point that it would be able to host another sensitive satellite payload is apparently too high to be worthwhile, at least from a perspective of economical reusability. The (quite literally) miniscule line that thus appears to be separating failed fairing recovery attempts from successes also means that it’s extraordinarily difficult to know whether the fairing half that returned on Mr. Steven yesterday morning is indicative of a breakthrough success or another successful failure.
Clearly, the fairing is perfectly intact from a purely structural perspective, meaning that its recovery hardware – cold gas thrusters and a parafoil – worked nominally. What is impossible to tell is whether its autonomous guidance systems were able to successfully direct it to Mr. Steven’s net, or whether Mr. Steven himself was able to maneuver beneath the falling fairing in time to catch it. And yet, a fairing half still sits visibly intact on Mr. Steven’s deck, story and fate unknown. With any luck, SpaceX will offer an official confirmation of some sort once success is in hand. For now, we wait.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!
Elon Musk
SpaceX shares targets and tentative launch date for Starship Flight 11
As with all SpaceX tests, the estimated timeline for Starship Flight 11 remains subject to change based on conditions and readiness.
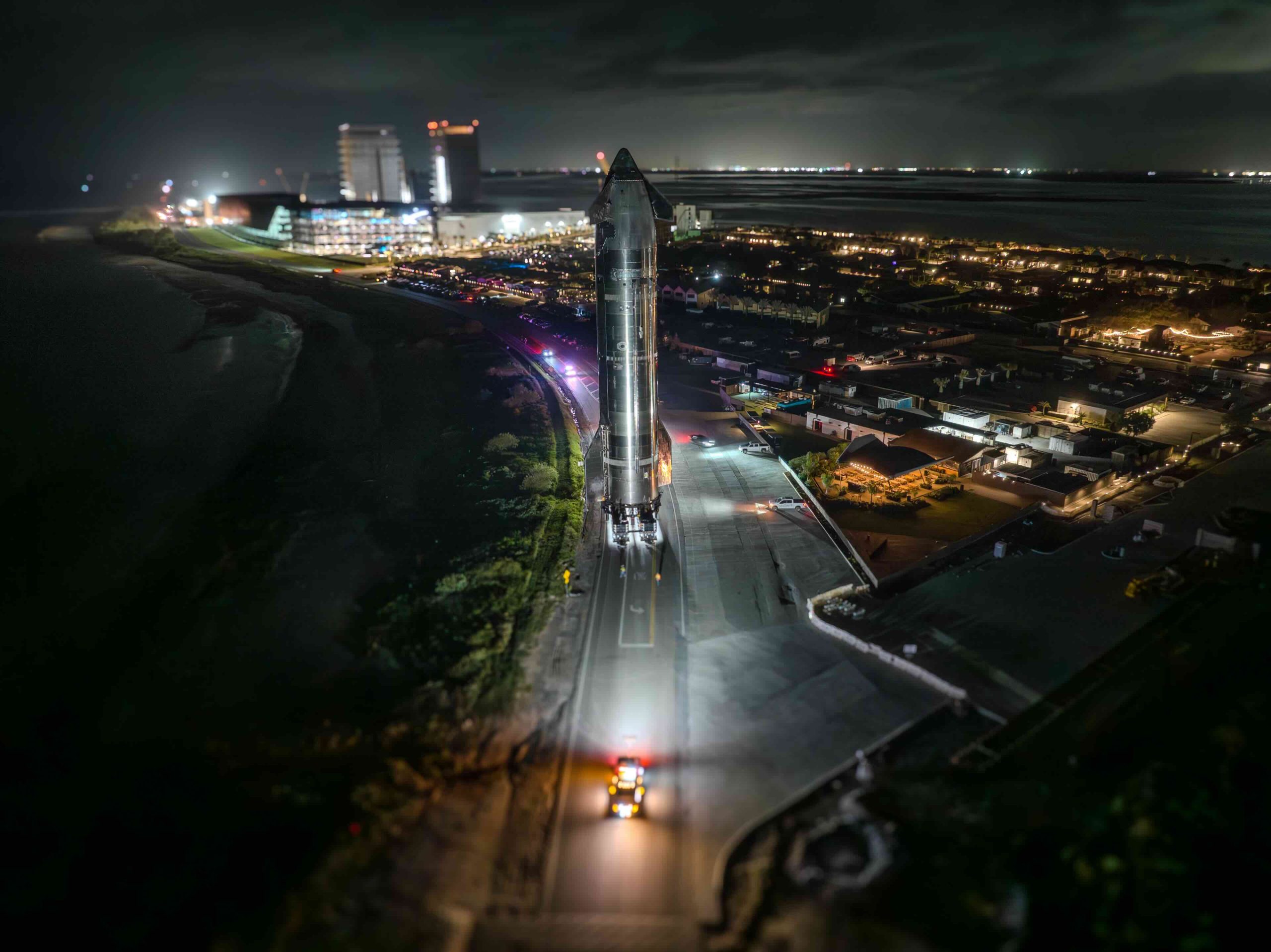

SpaceX is targeting Monday, October 13, for the eleventh test flight of its Starship launch system. The launch window is expected to open at 6:15 p.m. CT.
Similar to past Starship missions, a live webcast will begin about 30 minutes before launch on SpaceX’s website, X account, and X TV app. As with all SpaceX tests, the estimated timeline for Starship Flight 11 remains subject to change based on conditions and readiness.
Super Heavy booster landing test
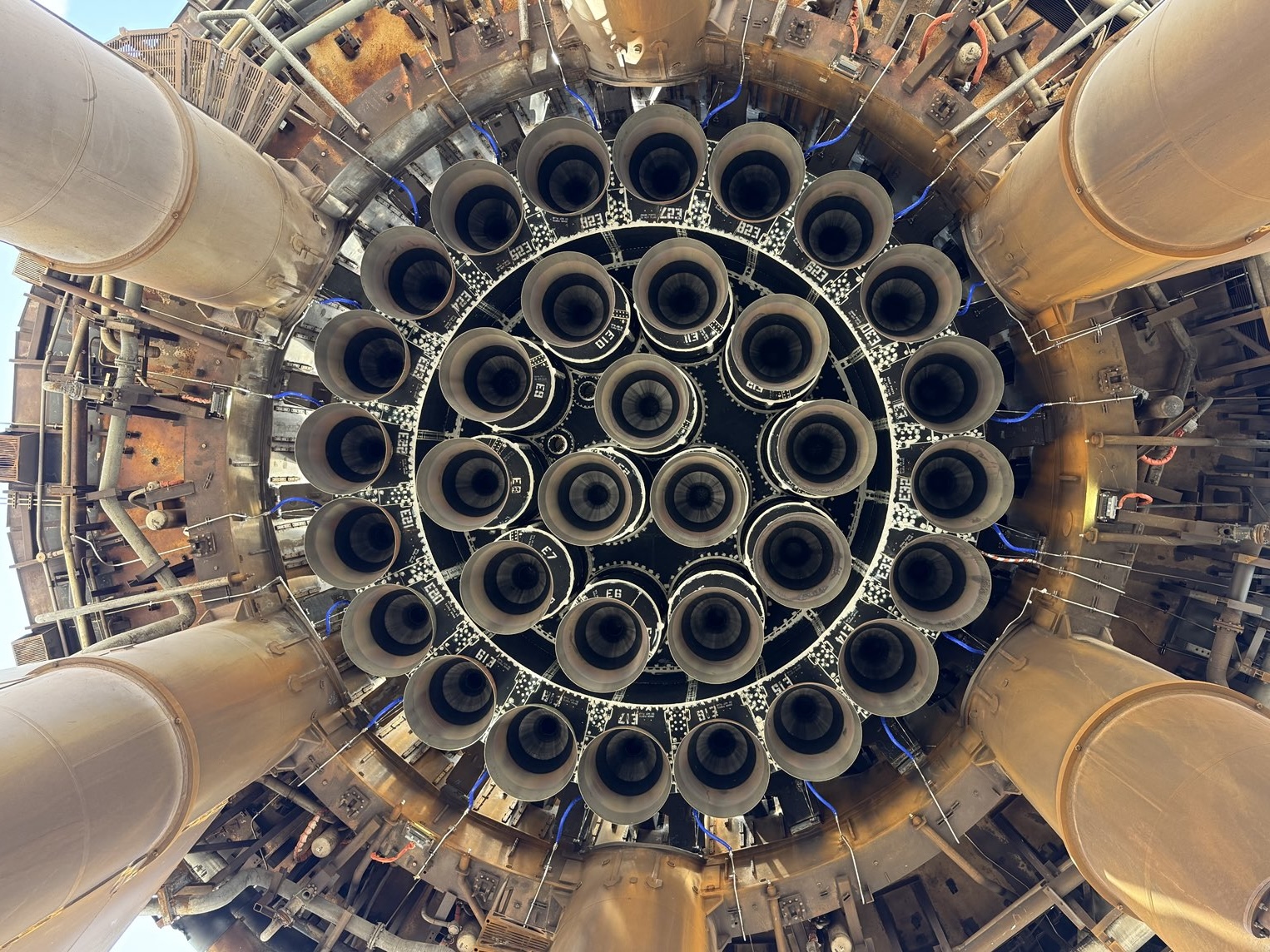
The upcoming mission will build on the data gathered from Starship’s tenth test flight, focusing on booster performance and upper-stage capabilities. The Super Heavy booster, previously flown on Flight 8, will launch with 24 flight-proven Raptor engines, according to SpaceX in a blog post on its official website. Its primary objective is to validate a new landing burn engine configuration designed for the next generation of Super Heavy.
Instead of returning to Starbase, the Super Heavy booster will follow a trajectory toward the Gulf of America. During descent, it will ignite 13 engines before transitioning to a five-engine divert phase and then completing the landing burn with three central engines, entering a full hover while still above the ocean surface, followed by shutdown and dropping into the Gulf of America.
Starship upper-stage experiments
The Starship upper stage for Flight 11 will carry out a series of in-space demonstrations, including the deployment of eight Starlink simulators that are comparable in size to next-generation Starlink satellites. These payloads will reenter and burn up during descent. A planned Raptor engine relight in orbit will also provide valuable test data.
To evaluate the upper stage’s resilience during reentry, SpaceX engineers have intentionally removed heat shield tiles from select areas to stress-test Starship’s thermal protection system. The vehicle will attempt new maneuvers during descent, including a banking profile and subsonic guidance algorithms intended to simulate future return-to-launch-site missions. The upper stage will ultimately target a splashdown in the Indian Ocean.
SpaceX has already posted a link to the livestream for Starship Flight 11:
News
Astra CEO shades SpaceX over employee workload and Starbase
Elon Musk once stated that no one ever changed the world working just 40 hours a week.

Elon Musk once stated that no one ever changed the world working just 40 hours a week. This was something that is openly known among his companies. They have the potential to change the world, but they require a lot of hours.
SpaceX’s working environment was recently criticized by Chris Kemp, the chief executive officer of Astra. During some remarks at the Berkeley Space Symposium 2025 earlier this month, Kemp shared some sharp remarks about the Elon Musk-led private space enterprise.
SpaceX working conditions and Starbase
As noted in a report from Ars Technica, Kemp discussed a variety of topics during his talk. These included Astra’s successes and failures, as well as his thoughts on other players in the spaceflight industry. To be fair to Kemp, he practically shaded every major rival, calling Firefly’s engine “garbage,” dubbing Blue Origin as slow, and stating that Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is “too small.”
SpaceX also received some colorful words from the Astra CEO. According to Kemp, SpaceX is leading the way in the spaceflight industry and Elon Musk is admirable in the way that he is willing to fail in order to move quickly. He did, however, highlight that Astra offers a significantly better working environment than SpaceX.
“It’s more fun than SpaceX, because we’re not on the border of Mexico where they’ll chop your head off if you accidentally take a left turn. And you don’t have to live in a trailer. And we don’t make you work six and a half days a week, 12 hours a day. It’s appreciated if you do, but not required,” Kemp said.
Elon Musk’s demands
It is known that Elon Musk demands quite a lot from his employees. However, it is also known that Musk-led companies move very fast and, in more ways than one, they have accomplished world-changing feats. Tesla, for example, has practically ushered in the era of the modern electric vehicle, and SpaceX has made space attainable through its reusable rockets. With this in mind, employees at Musk’s companies, and this of course includes SpaceX, are likely proud of their long work hours.
No one could probably go to Mars in this lifetime with a team that really works just 40 hours a week, after all.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk: Self-sustaining city on Mars is plausible in 25-30 years
Musk noted that true self-sufficiency requires Mars to develop “all the ingredients of civilization.”
Elon Musk has stated that a self-sustaining human settlement on Mars could be established in 25-30 years, provided launch capacity increases dramatically in the coming decades.
Speaking at the All-In Summit, the SpaceX CEO said building a self-sufficient colony depends on exponential growth in “tonnage to Mars” with each launch window, highlighting Starship’s role as the company’s pathway to interplanetary initiatives.
Mars settlement goals
Musk noted that true self-sufficiency requires Mars to develop “all the ingredients of civilization,” from food production to microchip manufacturing. Starship Version 3 is expected to support the first uncrewed Mars test flights, while future iterations could reach 466 feet in height and deliver larger payloads critical for settlement. Ultimately, Musk stated that an aggressive timeline for a city on Mars could be as short as 30 years, as noted in a Space.com report.
“I think it can be done in 30 years, provided there’s an exponential increase in the tonnage to Mars with each successive Mars transfer window, which is every two years. Every two years, the planets align and you can transfer to Mars.
“I think in roughly 15, but maybe as few as 10, but 10-15-ish Mars transfer windows. If you’re seeing exponential increases in the tonnage to Mars with each Mars transfer window, then it should be possible to make Mars self-sustaining in about call it roughly 25 years,” Musk said.
Starship’s role
Starship has flown in a fully stacked configuration ten times, most recently in August when it completed its first payload deployment in orbit. The next flight will close out the Version 2 program before transitioning to Starship Version 3, featuring Raptor 3 engines and a redesigned structure capable of lifting over 100 tons to orbit.
While SpaceX has demonstrated Super Heavy booster reuse, Ship reusability remains in development. Musk noted that the heat shield is still the biggest technical hurdle, as no orbital vehicle has yet achieved rapid, full reuse.
“For full reusability of the Ship, there’s still a lot of work that remains on the heat shield. No one’s ever made a fully reusable orbital heat shield. The shuttle heat shield had to go through nine months of repair after every flight,” he said.
-
 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoTesla FSD V14 set for early wide release next week: Elon Musk
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoElon Musk gives update on Tesla Optimus progress
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla has a new first with its Supercharger network
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoTesla job postings seem to show next surprise market entry
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla makes a big change to reflect new IRS EV tax credit rules
-

 Investor's Corner4 days ago
Investor's Corner4 days agoTesla gets new Street-high price target with high hopes for autonomy domination
-

 Lifestyle3 days ago
Lifestyle3 days ago500-mile test proves why Tesla Model Y still humiliates rivals in Europe
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoTesla Giga Berlin’s water consumption has achieved the unthinkable
























