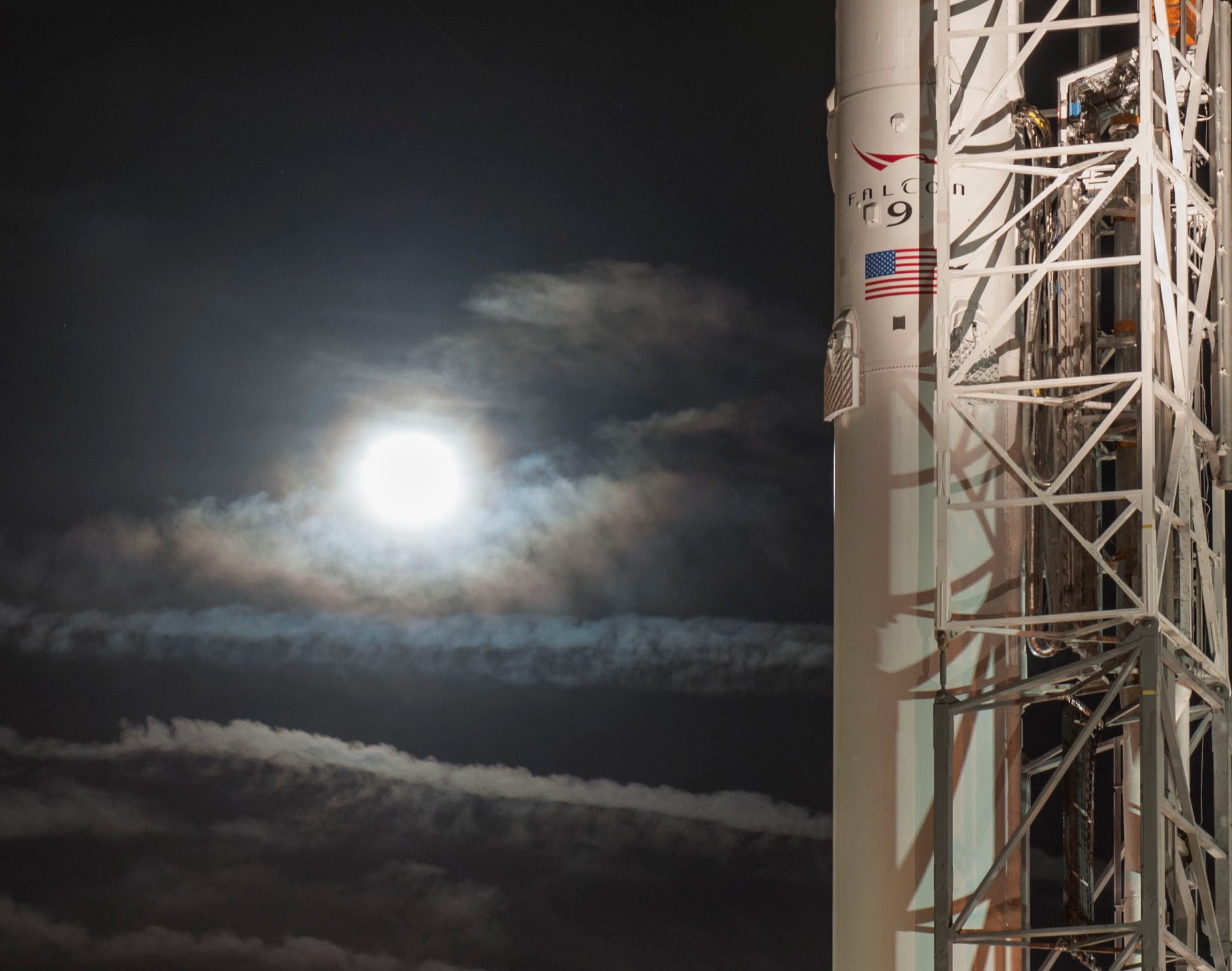
Josh Brost, Senior Director of SpaceX’s Government Business Development was in attendance at a civil spaceflight conference in Washington D.C. yesterday, January 18, and provided a number of interesting details about SpaceX’s upcoming activities in 2018. Perhaps most intriguingly, he reiterated SpaceX’s interest in enabling exploration of the Moon and Mars, while also clarifying that the upcoming Falcon 9 upgrade will be the last major change to the vehicle for the indefinite future.
Although the audience may have been more focused on SpaceX’s potential lunar prospects, Brost provided a vision similar to CEO Elon Musk’s common-knowledge goal of Martian (and interplanetary) colonization. This lunar focus was in part evidenced by a pointed question from an audience member that triggered Brost’s subsequent suggestion that the Moon could be a more logical starting place for the company as it ramps up its deep space efforts and gradually slips beyond Earth orbit. This strategic and calculated extension of the aspirations of the launch company’s famous founder is a rational attempt to position SpaceX in ways that allow the company to derive as much value as possible from the US government’s recently revived interest in returning the US and its astronauts to the Moon.
To a large extent, his comments mesh with the vision Elon Musk reiterated at 2017’s September IAC.
SpaceX’s next-generation heavy-lift rocket and spaceship (BFR and BFS) are being designed to carry 150 metric tons into low Earth orbit while still recovering both the first and second stages, and will be purpose-built for rapid and complete reusability. BFR and BFS are also being intentionally designed to be relatively destination-agnostic. In other words, BFS will be capable of transporting cargo and eventually crew to a number of destinations in the solar system, be it the Moon, Mars, or beyond. The outer planets are almost certainly off limits for crew due to the sheer length of any journey beyond the orbit of Mars, but BFR, as it was discussed last year, would be capable of transporting unprecedented amounts of cargo almost anywhere in the solar system. Reusability is, of course, paramount to SpaceX’s operational intent with BFR/BFS; unless a very lucrative offer is made, it is highly unlikely that SpaceX will even consider expendable missions, thus partially limiting what the next-gen vehicle will be capable of.
Still, it will be an incredibly capable rocket even with full reusability. Add in the potential promise of mature in-situ resource utilization (ISRU), more simply the production of methane and oxygen propellant at the destination, and it will open a hundred entirely new worlds to serious scientific, exploratory, and economic prospecting throughout the solar system.
What’s next?
The question, then, is “when?” While Brost did not specifically provide any sort of timeline for BFR, aside from a brief statement on its readiness in “a few years,” he did describe in some detail the imminent end of serious Falcon 9 upgrades. A continual stream of upgrades and modifications has been one of the only real constants with SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket: the original Falcon 9 is in almost every respect a completely different rocket when compared to the Falcon 9 Full Thrust (FT/1.2) of the present. However, one final leap is expected for Falcon 9, this time almost exclusively intended to improve the vehicle’s reliability and reusability as SpaceX rapidly approaches its first flights of Crew Dragon and dreams of rapid and repeated booster reuse.
While it was a small detail in an obscure sentence of one of several hour-long discussions, Brost specifically stated this:
Brost: with Block 5, goal it to lock down the design and fly the vehicle at very high flight rates. Innovation will focus on designing and testing BFR.
— Jeff Foust (@jeff_foust) January 18, 2018
This is arguably the most exciting tidbit provided to us by SpaceX. While it was undeniably vague and rather less than crystal-clear, it can be interpreted as something like this: once Block 5 has been introduced and begun to fly and refly both regularly and successfully, the vast majority of SpaceX’s launch vehicle development expertise will begin to focus intensely on the development and testing of BFR and BFS.
Statements from just last week made by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell strengthen this intuitive leap considerably, because BFR and BFS are liable to require a considerable amount of attention as they proceed through design maturation and eventually begin physical hardware testing in Texas.
Shotwell’s comments implied that SpaceX’s Boca Chica launch facilities, currently under construction, would be ready to support “vehicle tests” as early as late 2018/early 2019. Comments from earlier in 2017 indicate that SpaceX (and Shotwell) perceive Boca Chica as a near-perfect location for BFR launches (and thus BFR testing, as well). Finally, Brost’s implication that SpaceX’s exceptional team of brilliant and innovative launch vehicle engineers would be refocused on BFR soon after Block 5 was stable also meshes with this rough timeline. If Falcon 9 Block 5 does indeed debut within the “next few months” as Brost stated, it will have likely reached some level of design and operational maturity by the end of 2018, assuming SpaceX’s expected launch cadence.
As of right now, SpaceX is already looking at a very busy February, and currently has as many as three commercial launches scheduled within a period of maybe three weeks (GovSat-1, PAZ, and Hispasat), maybe even four if Falcon Heavy completes its first static fire later this weekend. Musk estimated that SpaceX would complete 30 missions in 2018, and a cadence anywhere near three launches per month (let alone four) would easily push SpaceX past that goal and provide the company dozens of opportunities to test, launch, recover, and relaunch their new Block 5 version of Falcon 9. As such, while BFR is probably not going to reach fully integrated hardware development or testing in 2018, it is certainly a distinct possibility, and 2019 is far more promising for the company’s interplanetary aspirations.
For now, SpaceX’s 2018 focus is quite explicitly centered on ensuring the reliability of its Crew Dragon – set to debut NET August 2018 – and Falcon 9 as it strives to complete the development of both vehicles. Up next on the company’s busy schedule is another attempt at Falcon Heavy’s inaugural static fire on Saturday afternoon, as well as the flight-proven launch of GovSat-1/SES-16, currently NET January 30.
Follow along live as launch photographer Tom Cross and I cover these exciting proceedings live from both coasts.
Teslarati – Instagram – Twitter
Tom Cross – Instagram
Eric Ralph – Twitter