SpaceX
SpaceX is about to get real busy: EchoStar and NASA on deck

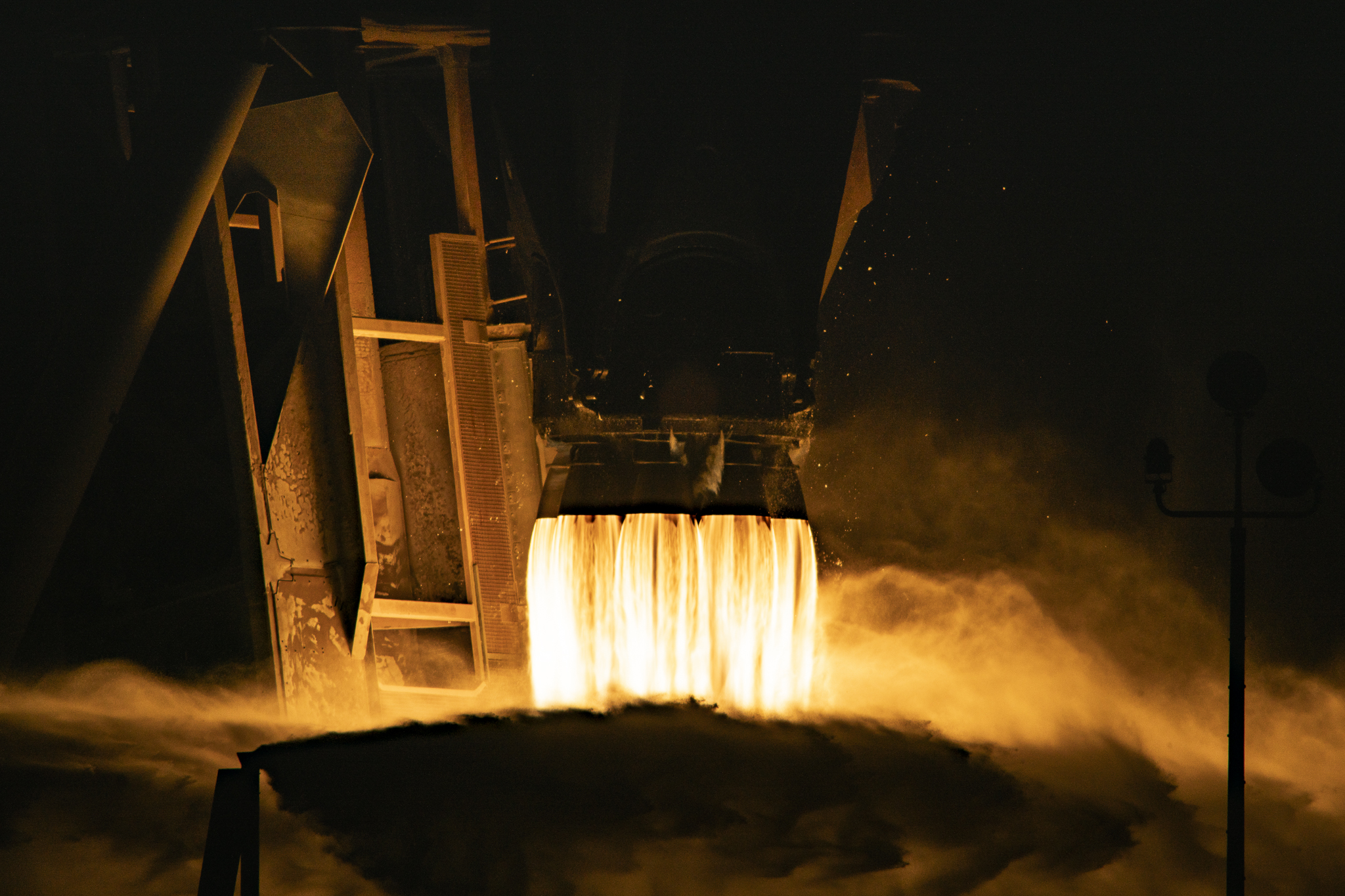
SpaceX ’s Falcon 9 return to flight (RTF) mission was a picture-perfect comeback, both figuratively and literally. On January 14, 2017, the company’s enthusiastic launch customer, Iridium, witnessed ten of its NEXT satellites deployed into orbit while Falcon 9’s first stage booster successfully landed onto its west coast droneship, “Just Read the Instructions”.
Elon Musk and SpaceX later tweeted a photograph of the landing that captured its spot-on landing, along with a link to a photo collection posted to SpaceX’s Flickr account.
Updated launch and landing photos → https://t.co/vn4S8bV3x3 pic.twitter.com/GRpm77LxKw
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) January 18, 2017
Now that the highly-anticipated RTF event has arrived, it’s time for Falcon 9 to march towards the next chapter of reusability. SpaceX has recovered seven first stage cores to date, most of which are potential candidates to be reused on a future mission.
On April 8, 2016, SpaceX completed its Falcon 9 Dragon cargo mission to resupply the International Space Station (ISS), and the first stage of its booster made history by successfully landing on a droneship for the first time. The same core recovered from that mission is now scheduled to make history once again and launch SES-10 no earlier than (NET) February 22, 2017.
SES-10, owned by SES of Luxembourg and built by Airbus Defense and Space, will be flown into geostationary orbit to provide telecom services to Latin America. Also notable, SES and SpaceX have history together: SES was SpaceX’s first commercial customer with the launch of SES-8 in December 2013. This relationship was acknowledged by Elon Musk when the contract for the refurbished booster was signed.
Thanks for the longstanding faith in SpaceX. We very much look forward to doing this milestone flight with you. https://t.co/U2UFez0OhY
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) August 30, 2016
SES previously confirmed that it received a discount for being the first customer to fly on a refurbished rocket. The satellite has reportedly been relocated to Florida after having been transferred from its manufacturing origin of Toulouse, France.
SES 10 isn’t SpaceX’s only mission in the coming weeks. Two other customers are awaiting their slot: EchoStar Corp. and NASA.
The next scheduled launch for Falcon 9 has been tentatively set for January 26th from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Its cargo will be EchoStar Corp’s EchoStar 23, a satellite providing Ku, Ka, and S-band communications capacity for direct-television broadcast services in Brazil. The company has been driven by a mid-2017 Brazilian regulatory deadline to begin broadcast services, thus Falcon 9’s restored flight status is a welcome relief.
The EchoStar 23 mission will be the first Falcon 9 launch conducted from historic Launch Complex 39A, former host of the Apollo missions. Pad 39A has been under construction since it was leased by SpaceX from NASA in April 2014, its primary intended purpose being that of hosting Falcon Heavy launches.
NASA also has another ISS cargo mission on the books with SpaceX, currently scheduled for February 8th. This will be the 10th Dragon cargo mission that SpaceX has been contracted for. While not scheduled to break any historical records, this mission is another reminder of both the working relationship SpaceX has with NASA and abilities as a serious launch provider heading towards transporting American astronauts into space.
Stay tuned as we bring you more coverage of upcoming booster landings and possibly a Falcon Heavy launch expected to take place later this year.
News
Starlink nears S Korea launch as satellite internet demand rises

Starlink is poised to launch in South Korea this year, pending regulatory approvals, as global demand for low-orbit satellite connectivity surges.
On April 27, South Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT announced system improvements to facilitate low-orbit satellite communication services like Starlink and the U.K.’s OneWeb. Low-orbit satellites, operating at 300–1,500 km, enable high-speed internet without extensive ground infrastructure, serving remote areas, ships, and airplanes.
“If we start domestic services, high-speed Wi-Fi services will be available on airplanes, and we will be able to provide online video services (OTT) and video calls to crews on long-haul ships,” said Minister of Science and ICT Yoo Sang-im.
According to KMIB, OneWeb is awaiting approvals for cross-border supply agreements and terminal suitability assessments. SpaceX’s Starlink is also waiting for approval. In October 2024, South Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT notified the public about amendments to technical standards that would prevent frequent interference. After 60 days of the notice’s publication, the South Korean government is estimated to take 3-4 months to approve Starlink’s cross-board supply agreement with SpaceX.
Kim Nam-cheol, director of the Radio Policy Bureau, noted, “It is certain that (the two companies) will launch services this year, but it is difficult to specify a date as changes may occur during the consultation process.”
Starlink and OneWeb’s pending approvals in S. Korea involve ensuring compliance with local regulations, including terminal assessments for new devices. The push for satellite internet reflects a broader global trend, with S. Korea positioning itself to bridge connectivity gaps in aviation, maritime, and remote regions.
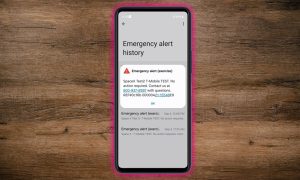
Starlink’s global reach is evident, and its usefulness increases as it expands. In January, T-Mobile used Starlink Cellular to transmit emergency alerts during LA wildfires. Meanwhile, Hawaiian and United Airlines offer Starlink Aviation for in-flight video streaming and gaming.
As Starlink expands, new competitors enter the ever-growing lob-orbit satellite communications industry. For example, Amazon’s Kuiper established a corporation in South Korea last May.
Starlink’s involvement in the Ukriane-Russia war has also led world governments to consider establishing their own satellite communications network. South Korea aims to develop its own independent satellite technology by 2030. The Asian nation plans to invest 320 billion won over six years to launch two communication units via the Nuri rocket.
Ukraine is also exploring Starlink alternatives developed by the European Union. In addition, Germany’s military, Bundeswehr, plans to build its own satellite constellation to reduce dependence on foreign networks amid geopolitical tensions.
As Starlink expands, S Korea’s regulatory and technological efforts could shape its role in the global satellite communication market, balancing foreign services with ambitions for domestic innovation.
News
Starlink India’s license faces delay due to regulatory requirements

SpaceX’s satellite internet venture Starlink has yet to secure an operating license in India. Starlink is facing regulatory delays in India despite ongoing progress.
India’s Telecom Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia confirmed that the company must meet stringent requirements before launching services in the country.
“The process is ongoing. The minute they meet all conditions — including setting up gateways in India and registering user terminals locally — we are ready to issue the license,” Scindia told local media.
The licensing process involves multiple agencies in India, including the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), and the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe). These agencies are evaluating Starlink’s compliance with India’s technical, administrative, and national security standards.
Scindia emphasized Starlink’s need for domestic registration of user terminals and local gateways to address data sovereignty and internal security concerns.
“It’s not only related to DoT but also to internal security — gateways have to be in India, any user terminal has to be registered in India…the minute they check all the boxes, which I also hope will be soon, the license should be given,” he added.
The requirements reflect India’s cautious approach to integrating foreign satellite providers into its telecom ecosystem. The delay comes amid broader industry calls for enhanced connectivity. At Mobile World Congress 2025 in Barcelona, Bharti Airtel chairman Sunil Mittal urged regulators to support telecom operators in closing the global connectivity gap for 400 million people, particularly in rural India. He advocated for resource sharing between terrestrial and satellite operators to avoid duplicative investments.
Bharti Airtel and Jio Platforms signed agreements with SpaceX to help expand Starlink services in India. The agreements are contingent on the Indian government approving Starlink’s license.
Starlink’s potential entry into India could bolster rural connectivity, but regulatory hurdles remain a significant barrier. As the company works to meet India’s conditions, its progress is closely watched by telecom operators and regulators alike. The outcome could shape the role of satellite internet in addressing India’s digital divide, aligning with global efforts to expand access through collaborative infrastructure investments.
News
SpaceX investment fuels Alphabet’s $8 billion profit surge

Alphabet Inc.’s first-quarter profit soared, boosted by an $8 billion unrealized gain from its investment in SpaceX. Since 2015, Alphabet has been a key SpaceX investor, joining Fidelity Investments to inject $1 billion for a 10% stake in the space firm.
The tech giant reported a 46% surge in net income to $34.54 billion, driven by strong advertising revenues and the SpaceX windfall, Bloomberg reported Thursday, citing a person familiar with the matter. SpaceX’s valuation hit approximately $350 billion in December, cementing its status as one of the world’s most valuable private companies. The company thrives on NASA contracts and its Starlink satellite internet service, which provides direct-to-consumer connectivity.
Unlike Tesla, SpaceX has largely sidestepped public backlash tied to CEO Elon Musk despite growing scrutiny. The Tesla Takedown movement, emboldened by Tesla’s first-quarter 2025 earnings, plans to target Musk’s other ventures, including SpaceX and Starlink.
Starlink faces its own challenges abroad. For instance, Ukraine is exploring Starlink alternatives developed by the European Union. Ukraine and EU member states have become increasingly worried about Elon Musk, which is being reflected in SpaceX’s Starlink contracts on the continent. However, Starlink remains critical for Ukraine’s battlefield connectivity, with EU alternatives lagging behind SpaceX’s robust internet capabilities.
Alphabet’s financial windfall underscores SpaceX’s growing influence in the space and satellite internet sectors. The $8 billion gain from “non-marketable equity securities,” identified as SpaceX, highlights the strategic value of Alphabet’s early investment. While Tesla grapples with public and activist scrutiny, SpaceX’s government contracts and Starlink’s consumer reach provide a buffer, though not immunity, from Musk-related controversies.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla’s Hollywood Diner is finally getting close to opening
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla doubles down on Robotaxi launch date, putting a big bet on its timeline
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla is trying to make a statement with its Q2 delivery numbers
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s top investor questions ahead of the Q1 2025 earnings call
-

 Investor's Corner1 week ago
Investor's Corner1 week agoLIVE BLOG: Tesla (TSLA) Q1 2025 Company Update and earnings call
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla police fleet saves nearly half a million in upkeep and repair costs
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoGlobal EV sales climbed 29% in March, powered by China & Europe
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla reportedly suspended Cybercab and Semi parts order amid tariff war: Reuters